7 Key Canine Autoimmune Diseases and Their Treatments
In your search for canine autoimmune diseases and their treatments, here are the key points: Canine autoimmune hemolytic anemia involves managing the immune system attacking red blood cells. Treatment includes managing symptoms effectively. For canine immune-mediated polyarthritis, medication and physical therapy are crucial. Systemic lupus erythematosus affects various organs and requires symptom management with medications. Dogs with immune-mediated thrombocytopenia may need corticosteroids to suppress platelet destruction. Addison's disease impacts adrenal glands and needs hormone replacement therapy. Hypothyroidism calls for synthetic thyroid hormones. Pemphigus foliaceus necessitates immunosuppressive medications for skin issues. Prompt management is vital for these conditions.
Canine Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
Discussing the treatment options for Canine Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia involves addressing the complexities of managing this condition effectively while considering the individual needs of each affected dog. This autoimmune disease occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its red blood cells, leading to severe anemia. Common symptoms of this condition include weakness, pale gums, lethargy, and jaundice. If left untreated, Canine Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia can be life-threatening.
To diagnose this condition, your veterinarian may perform a series of tests such as bloodwork, a Coombs test, and a reticulocyte count. Once diagnosed, the prognosis for Canine Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia can vary depending on the severity of the disease and how well your dog responds to treatment.
Treatment options for Canine Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia typically involve a combination of immunosuppressive drugs like corticosteroids to suppress the immune system's attack on red blood cells. In some cases, other medications such as azathioprine or cyclosporine may be prescribed. Blood transfusions may also be necessary to stabilize your dog if they're severely anemic. Monitoring your dog's response to treatment through regular check-ups and blood tests is crucial to adjust the treatment plan as needed and improve their overall prognosis. It's essential to work closely with your veterinarian to manage this condition effectively and provide the best possible care for your furry companion.
Canine Immune-Mediated Polyarthritis
Canine Immune-Mediated Polyarthritis commonly presents as inflammation in multiple joints of dogs, causing pain and mobility issues. This autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, leading to swelling, stiffness, and lameness in affected dogs. Treatment options for Canine Immune-Mediated Polyarthritis typically involve a combination of medications to reduce inflammation and manage pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to alleviate discomfort and improve mobility. In more severe cases, immunosuppressive drugs such as corticosteroids may be necessary to modulate the immune response and reduce joint inflammation.
The prognosis for dogs with Canine Immune-Mediated Polyarthritis varies depending on the severity of the condition and the response to treatment. With prompt diagnosis and appropriate management strategies, many dogs can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life. Regular veterinary monitoring is crucial to adjust treatment protocols as needed and ensure the best possible outcome for the affected dog.
In some instances, case studies have shown that a multimodal approach combining medication with physical therapy and weight management can further enhance the effectiveness of treatment for Canine Immune-Mediated Polyarthritis. This comprehensive approach not only targets the inflammation in the joints but also focuses on improving muscle strength and joint function to support long-term joint health and mobility.
Canine Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in dogs is a complex autoimmune disease that can affect various organs and systems in the body. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues, leading to inflammation and damage.
Canine lupus symptoms can vary widely but commonly include:
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Dogs with lupus may experience lameness, stiffness, and swelling in their joints, resembling symptoms of arthritis.
- Skin Lesions: Skin issues like redness, hair loss, and ulcers can be present in dogs with lupus, particularly on the face and ears.
- Fever and Lethargy: Some dogs may exhibit a persistent fever, along with weakness and lack of energy, indicating systemic inflammation.
When it comes to lupus treatment options for dogs, the goal is to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and suppress the immune response. Veterinarians may prescribe medications such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to help control the disease. Additionally, supportive care like a balanced diet, exercise, and regular veterinary check-ups are essential to monitor the progression of the disease and adjust treatment as needed.
If you notice any unusual symptoms in your dog, such as joint pain, skin issues, or lethargy, it's crucial to consult with your veterinarian promptly for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Canine Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia
Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia in dogs is a condition characterized by the immune system destroying platelets, crucial for blood clotting. Platelet destruction occurs when the immune response mistakenly targets these essential blood components, leading to a decreased platelet count in the bloodstream. This condition can result in excessive bleeding and bruising in affected dogs.
The underlying causes of Canine Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia aren't always clear, but it's believed to be triggered by an abnormal immune response. The immune system normally protects the body from harmful invaders, but in this case, it mistakenly identifies platelets as threats, leading to their destruction. Certain breeds, such as Cocker Spaniels, are more predisposed to this condition.
Treatment options for Canine Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia aim to suppress the immune response to prevent further destruction of platelets. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are commonly prescribed to reduce immune activity. Other immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine may also be used in more severe cases. In some instances, blood transfusions or platelet transfusions may be necessary to manage bleeding episodes and support the dog's blood clotting function.
Regular monitoring of platelet counts and overall health is essential for dogs with Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia to adjust treatment plans as needed and ensure the best possible outcome for the affected pet.
Canine Addison's Disease
Frequently overlooked in dogs, Addison's Disease affects the adrenal glands' ability to produce essential hormones. This condition, also known as hypoadrenocorticism, can lead to a range of symptoms that, if left untreated, can be life-threatening.
Here are key points to consider regarding Canine Addison's Disease:
- Symptoms: Canine Addison's Disease can present with vague signs such as lethargy, decreased appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, and weight loss. In severe cases, dogs may experience collapse, weakness, and dehydration.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosing Addison's Disease in dogs can be challenging as the symptoms are nonspecific. Veterinary assessment typically involves blood tests to evaluate electrolyte levels and adrenal function. Additional tests like ACTH stimulation tests may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
- Prognosis: With appropriate management, which often includes hormone replacement therapy, dogs with Addison's Disease can lead normal lives. Regular veterinary check-ups and monitoring are crucial to adjust medication dosages as needed.
Canine Addison's disease management focuses on replacing the deficient hormones (corticosteroids and mineralocorticoids) to restore balance in the body. It's essential for dog owners to be vigilant for any recurrence of symptoms and to work closely with their veterinarian to ensure the best possible outcome for their furry companion.
Canine Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism in dogs commonly manifests as a deficiency in thyroid hormone production, impacting various bodily functions. This condition is often caused by autoimmune destruction of the thyroid gland, leading to reduced hormone levels. Common symptoms of canine hypothyroidism include weight gain, lethargy, hair loss, skin problems, and intolerance to cold temperatures. If left untreated, hypothyroidism can result in serious complications affecting the heart, skin, and metabolism of the dog.
Fortunately, there are effective treatment options available for canine hypothyroidism. The primary treatment involves hormone replacement therapy using synthetic thyroid hormones, such as levothyroxine. This medication helps restore the hormone levels in the body, alleviating the symptoms and improving the overall health of the dog. It's essential to follow the veterinarian's instructions regarding dosage and administration to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
Regular monitoring of the dog's thyroid hormone levels is crucial to adjust the medication dosage as needed and ensure optimal management of the condition. In addition to medication, maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise can support the treatment of canine hypothyroidism. By working closely with your veterinarian and following the prescribed treatment plan, you can help manage hypothyroidism in your dog effectively and improve their quality of life.
Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus
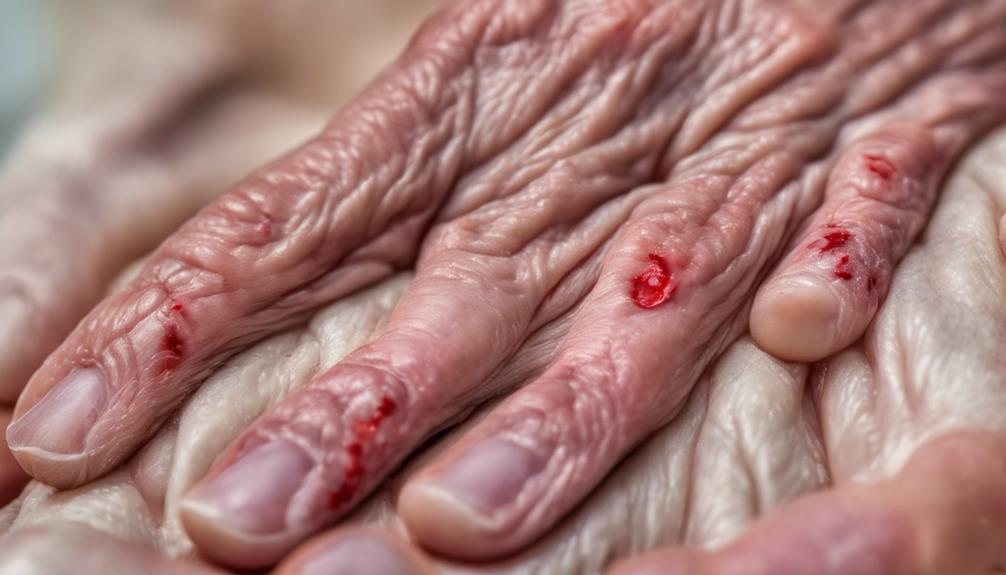
Pemphigus Foliaceus is a skin disease in dogs characterized by the formation of blisters and sores, primarily affecting the superficial layers of the skin. This autoimmune condition occurs when the dog's immune system mistakenly attacks proteins in the skin, leading to the separation of skin cells and the development of lesions.
Treatment Options: Veterinarians typically treat Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus with immunosuppressive medications such as corticosteroids to suppress the immune system's abnormal response. Other medications like azathioprine or cyclosporine may also be used to manage the condition. In severe cases, additional treatments like antibiotics or topical therapies may be necessary to control secondary infections or promote skin healing.
Prognosis: The prognosis for dogs with Pemphigus Foliaceus varies depending on the severity of the disease and the dog's response to treatment. With prompt diagnosis and appropriate management, many dogs can achieve long-term remission and lead comfortable lives. However, relapses can occur, requiring ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan.
Disease Triggers and Prevention: While the exact triggers for Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus aren't fully understood, genetic predisposition and environmental factors may play a role in its development. Preventive measures focus on managing potential triggers like infections, medications, or stressors that could exacerbate the autoimmune response, thus reducing the risk of disease onset. Regular veterinary check-ups and early intervention are essential in maintaining the overall health and well-being of dogs susceptible to autoimmune conditions like Pemphigus Foliaceus.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Diet and Nutrition Affect the Severity of Autoimmune Diseases in Dogs?
Yes, diet and nutrition can significantly impact the severity of autoimmune diseases in dogs.
By incorporating the right supplements and making appropriate dietary modifications, you can positively influence your dog's immune response and reduce the inflammatory response associated with autoimmune conditions.
Ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet tailored to your dog's specific needs can play a crucial role in managing autoimmune diseases effectively.
Are There Alternative Treatment Options Available for Canine Autoimmune Diseases?
When dealing with canine autoimmune diseases, you might want to explore alternative treatment options. Natural remedies and a holistic approach can sometimes complement traditional treatments. These methods focus on supporting your dog's overall health and immune system.
While not a replacement for medical interventions, incorporating holistic practices can sometimes provide additional support and improve your furry friend's well-being. It's essential to consult with your vet to determine the best course of action for your pup.
Can Stress or Environmental Factors Trigger Autoimmune Diseases in Dogs?
Stress and environmental factors can indeed trigger autoimmune diseases in dogs. These stressors can disrupt the immune system, leading to misguided attacks on the body's tissues.
While the exact mechanisms are complex, managing these triggers is crucial. Immunotherapy, along with identifying and minimizing environmental stressors, plays a key role in long-term management of canine autoimmune diseases.
It's essential to create a low-stress environment to support your dog's immune system health.
Is There a Genetic Predisposition for Autoimmune Diseases in Certain Dog Breeds?
Yes, there's a genetic predisposition for autoimmune diseases in certain dog breeds. Breed correlation plays a significant role in the likelihood of developing these conditions. Specific breeds may have a higher risk due to their genetic makeup.
Understanding these genetic factors can help in early detection and management of autoimmune diseases in dogs. Regular veterinary check-ups and genetic testing can assist in identifying potential risks and providing appropriate care for predisposed breeds.
How Can Pet Owners Prevent Relapses of Autoimmune Diseases in Their Dogs?
To prevent relapses of autoimmune diseases in your dogs, try incorporating an exercise regimen to boost their overall health and immune system.
Behavioral therapy can help reduce stress levels, which may trigger flare-ups.
Additionally, consider herbal remedies or acupuncture as complementary treatments to support your dog's well-being.
These holistic approaches can aid in managing symptoms and promoting a healthier lifestyle for your furry companion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, canine autoimmune diseases can be complex and challenging to manage, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, many dogs can live happy and healthy lives.
It's important for pet owners to be aware of the signs and symptoms of these diseases and work closely with their veterinarian to develop a treatment plan tailored to their dog's specific needs.
With proper care and monitoring, dogs with autoimmune diseases can still enjoy a good quality of life.
